Description
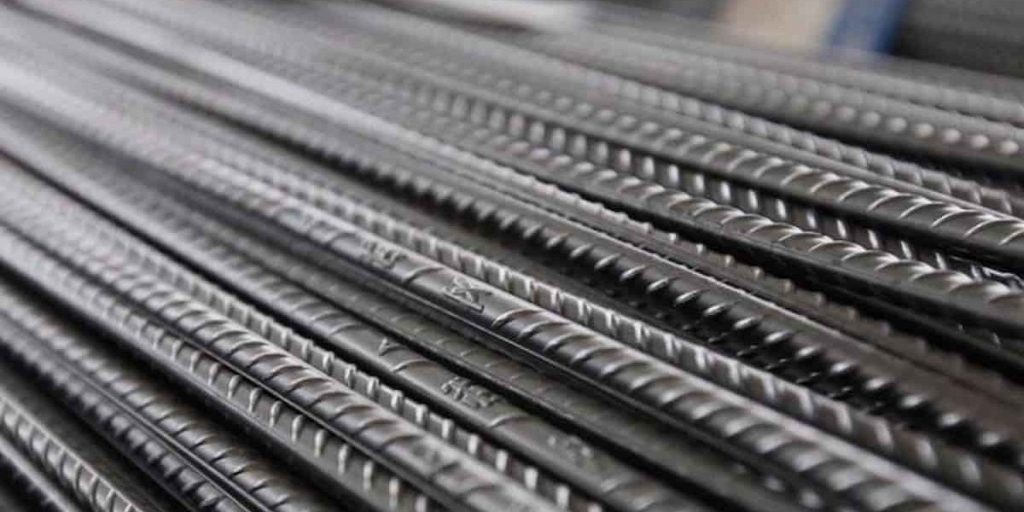
1. What is a steel rebar?
Steel rebar, short for reinforcing bar, is a steel bar or mesh of steel wires used as a tension device in reinforced concrete and reinforced masonry structures. It is used to strengthen and hold the concrete in tension. Here are some key points about steel rebar:
Purpose
- Reinforcement: Concrete is strong in compression but weak in tension. Rebar is used to enhance the tensile strength of the structure.
- Crack Control: Helps in controlling cracks in concrete by providing additional strength.
Types
- Mild Steel Rebar: Traditional form made from carbon steel, known for its strength and flexibility.
- Deformed Rebar: Has ridges, ribs, or deformations on the surface to provide better mechanical anchoring in concrete.
- Epoxy-Coated Rebar: Coated with epoxy to resist corrosion, often used in environments exposed to moisture and salt.
- Stainless Steel Rebar: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and is used in high-stress environments.
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) Rebar: Non-metallic alternative used in structures requiring non-corrosive reinforcement.
Sizes and Grades
- Sizes: Rebar comes in various sizes, typically ranging from #3 (3/8 inch) to #18 (2-1/4 inches) in diameter in the U.S.
- Grades: Different grades indicate yield strength, typically ranging from Grade 40 to Grade 120 in the U.S.
Applications
- Building Foundations: Used in the foundation to provide stability and strength.
- Bridges and Overpasses: Provides tensile strength in structures subjected to dynamic loads.
- Roadways and Pavements: Enhances durability and load-bearing capacity.
- Retaining Walls: Offers support and resistance to lateral forces.
Installation
- Cutting and Bending: Rebar is often cut and bent to specific shapes to fit the design requirements.
- Tying: Rebar is typically tied together using steel wire to hold it in place during concrete pouring.
Steel rebar plays a critical role in modern construction, providing the necessary support to concrete structures to ensure their integrity and longevity.
2. What are the technologies used in steel rebar production?
Steel rebar production involves several technological processes to ensure the reinforcement bars meet specific standards for construction use. Here’s an overview of the main technologies and methods involved in steel rebar production:
- Reheating Furnace: The billets are reheated to the desired temperature to make them malleable for shaping.
- Hot Rolling: The heated billets are passed through a series of rolling mills, which shape them into the desired rebar sizes and profiles. This process aligns the microstructure, enhancing mechanical properties.
- Thermo-Mechanical Treatment (TMT) Process: Involves a combination of controlled cooling and reheating of the hot-rolled rebar to improve its strength and ductility. The TMT process enhances the rebar’s yield strength, elongation, and weldability.
- Quenching: The rebar surface is rapidly cooled using water jets to form a hardened outer layer while maintaining a softer core.
- Tempering: The rebar is then allowed to cool slowly, reducing internal stresses and increasing toughness.
- Cold Twisting or Drawing: Some rebar undergo cold working processes like twisting or drawing to enhance mechanical properties further.
– Quality Control and Testing
- Mechanical Testing: Rebar samples are tested for tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and bending properties.
- Chemical Testing: The chemical composition is analyzed to ensure compliance with standards.
- Dimensional Checks: Rebar dimensions are checked for accuracy and conformity to specifications.
– Packaging and Distribution
- Bundling: Finished rebars are bundled and tagged for identification and traceability.
- Transportation: Rebars are distributed to construction sites or storage facilities.
– Innovations and Trends
- Advanced Alloys: Development of new steel alloys for improved strength and corrosion resistance.
- Sustainability Practices: Incorporation of energy-efficient processes and increased use of recycled materials.
- Automation and Robotics: Use of automated systems for precision in rolling, cutting, and handling rebars.
- Quality Monitoring Technologies: Use of sensors and AI for real-time monitoring and quality control.
These technologies and processes ensure that steel rebars meet the structural requirements for various construction projects, offering strength, durability, and reliability.
3. What are the advantages of steel rebar?
Steel rebar, or reinforcing bar, is a critical component in construction, particularly in reinforced concrete structures. It offers several advantages that make it the preferred choice for reinforcement in various construction projects. Here are the key advantages of steel rebar:
1. High Tensile Strength
- Reinforcement: Steel rebar has high tensile strength, making it ideal for reinforcing concrete, which is strong in compression but weak in tension. This combination enhances the overall structural integrity.
- Load Bearing: It effectively handles tensile forces, improving the load-bearing capacity of concrete structures.
2. Ductility
- Flexibility: Steel rebar can withstand significant deformation without losing strength, allowing structures to absorb energy from forces such as seismic activities.
- Resilience: Its ductility ensures that structures can withstand various stresses and strains without cracking or failing abruptly.
3. Bonding with Concrete
- Adhesion: The ribbed or deformed surface of steel rebar ensures a strong bond with concrete, preventing slippage and enhancing structural stability.
- Integration: This strong bond helps in transferring loads effectively between the concrete and the rebar.
4. Corrosion Resistance
- Coatings: Steel rebar can be coated with materials like epoxy or galvanized with zinc to resist corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
- Durability: Properly treated rebar enhances the longevity of structures by minimizing rust and corrosion-related damage.
5. Availability and Versatility
- Wide Range: Rebar is available in various sizes, grades, and types, making it versatile for different construction needs.
- Customizability: It can be bent, cut, and shaped to fit specific design requirements, allowing for creative architectural solutions.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
- Economical: Steel rebar offers a cost-effective solution for reinforcing concrete structures due to its long-lasting performance and durability.
- Minimal Maintenance: Once embedded in concrete, it requires minimal maintenance, reducing long-term costs.
7. Thermal Expansion Compatibility
- Similar Coefficient: Steel and concrete have similar coefficients of thermal expansion, reducing the risk of cracking due to temperature changes.
- Stability: This compatibility ensures that temperature fluctuations do not adversely affect the structural integrity.
8. Fire Resistance
- Performance under Heat: Steel rebar can withstand high temperatures, helping maintain structural stability in the event of a fire.
- Safety: Its performance under fire conditions enhances the safety of buildings and infrastructure.
9. Environmental Benefits
- Recyclability: Steel is 100% recyclable, making rebar an environmentally friendly choice. It can be reused and repurposed without losing quality.
- Sustainability: Using recycled steel in rebar production reduces the demand for raw materials and energy, contributing to sustainable construction practices.
10. Strength-to-Weight Ratio
- Efficiency: Steel rebar has a high strength-to-weight ratio, meaning it provides significant reinforcement without adding excessive weight to structures.
- Design Flexibility: This allows for more efficient design and construction, especially in tall buildings and bridges.
In Summary, Steel rebar plays a crucial role in reinforcing concrete structures by providing tensile strength, durability, and flexibility. Its corrosion resistance, thermal expansion compatibility, and recyclability make it an attractive option for sustainable construction. Moreover, its cost-effectiveness and versatility ensure that it remains a key component in the construction industry, helping create safe and resilient structures.
4. What is the supply capacity of Avina Export Group?
In Iran, there are more than 50 steel rebar production factories, with the largest production volumes concentrated in the provinces of East Azerbaijan, Zanjan, Isfahan, and Khuzestan. In 2023, Iran’s steel rebar production reached over 10 million tons, marking the highest output in the country’s history. The geographical distribution of these producers across Iran allows the desired rebar to be supplied from the nearest border point, depending on the export customer’s destination. This reduces transportation costs for the customer.
Avina Export Group has strong relationships with steel rebar producers across the four corners and the center of Iran, enabling us to supply high tonnages at competitive prices with on-time delivery to our valued customers. We offer a wide range of steel rebar produced with high quality and competitive pricing according to our customers’ needs. Additionally, custom products are available in large quantities upon customer request.
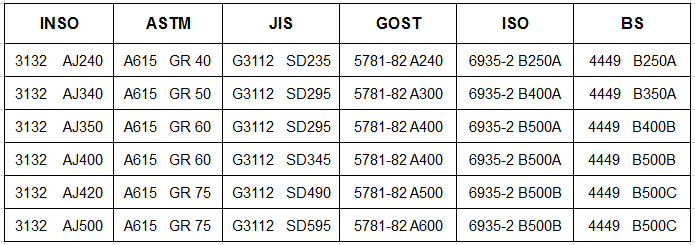
5. What are the standards for steel rebar?
Steel rebar standards vary by country and organization, each providing specifications and guidelines for manufacturing, testing, and using reinforcing bars in construction. These standards ensure consistency, quality, and safety across construction projects. Here’s an overview of some key standards and their features:
1. ASTM Standards (American Society for Testing and Materials):
- ASTM A615: This standard covers deformed and plain carbon-steel bars for concrete reinforcement. It specifies requirements for deformations (ridges), chemical composition, and mechanical properties like tensile strength and yield strength.
- ASTM A706: This is a specification for low-alloy steel deformed and plain bars for concrete reinforcement, designed to be more ductile and weldable than bars produced to A615.
- ASTM A996: This standard specifies rail-steel and axle-steel deformed bars for concrete reinforcement.
- ASTM A1035: This standard covers low-carbon, chromium, steel-reinforced bars that have superior corrosion resistance.
2. BS Standards (British Standards):
- BS 4449: This standard specifies requirements for ribbed steel reinforcing bars used in the UK. It outlines mechanical properties, including yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation, and categorizes bars into different grades.
- BS 4482: This standard covers cold-reduced steel wire for the reinforcement of concrete and specifies requirements for weldable steel.
3. EU Standards (European Standards):
- EN 10080: This European standard specifies general requirements for reinforcing steel, including bar, wire rod, and welded fabric. It covers mechanical properties, chemical composition, and performance.
- EN 1992 (Euro code 2): Although not a standard for rebar itself, Euro code 2 outlines design requirements for concrete structures, including the use of rebar.
4. ISO Standards (International Organization for Standardization):
- ISO 6935-2: This standard specifies technical requirements for ribbed bars used in concrete reinforcement. It includes provisions for mechanical properties, such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility, as well as specifications for chemical composition.
5. DIN Standards (German Standards):
- DIN 488: This standard is used in Germany and covers reinforcing steels, detailing the specifications for ribbed bars, including their mechanical properties and performance requirements.
6. GOST Standards (Russian Standards):
- GOST 5781: This standard covers hot-rolled steel bars with periodic profiles used in concrete reinforcement. It includes requirements for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface deformations.
6. What do you know about Iranian steel rebar?
Iran is one of the leading producers and exporters of steel rebar in the world. Steel rebar, also known as reinforcing bar, is used primarily in construction to reinforce concrete and masonry structures. Here’s what you should know about Iranian steel rebar:
1. Production Capacity:
Iran has a significant steel production capacity, and rebar is one of the key products in this industry. The country ranks among the top steel producers globally, and its production has been steadily increasing over the years.
2. Quality Standards:
Iranian steel rebar is produced according to various international standards, such as ASTM, BS, and DIN, ensuring that the products meet global quality requirements. The rebar typically comes in different grades, which indicate the tensile strength and chemical composition.
3. Export Markets:
Iran exports a substantial portion of its steel rebar production to various countries, especially in the Middle East, Asia, and Africa. Despite international restrictions, Iran has managed to maintain a strong presence in these markets.
4. Price Competitiveness:
Iranian steel rebar is often competitively priced due to the relatively low cost of production in the country. This has made it a preferred choice in many emerging markets where cost is a critical factor.
5. Domestic Demand:
Domestically, Iran’s construction sector is a significant consumer of steel rebar, driven by infrastructure projects and housing developments. Government initiatives to boost construction and housing have also fueled demand.
6. Environmental Considerations:
Like many steel-producing nations, Iran is also dealing with environmental concerns related to steel production, including carbon emissions and energy consumption. Efforts to improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental footprint of the industry are ongoing.
In summary, Iranian steel rebar is an important product in both domestic and international markets, known for its competitive pricing and adherence to global quality standards.
7. To which countries is Iranian steel rebar exported?
Iran exports steel rebar to a variety of countries, particularly in regions where cost-effective construction materials are in high demand. Here are some of the key destinations for Iranian steel rebar exports:
1. Middle East:
- Iraq: A significant importer of Iranian steel rebar, largely due to the proximity and the need for reconstruction and infrastructure development.
- Afghanistan: Another major destination, driven by the ongoing construction projects and the need for affordable building materials.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): While the UAE is a regional trading hub with its own steel production capabilities, it also imports steel rebar from Iran, particularly when there are favorable trade conditions.
2. Asia:
- Oman: Iran exports a considerable amount of steel rebar to Oman, benefiting from strong trade relations and geographical proximity.
- Pakistan: Another neighboring country that imports Iranian rebar, supporting its growing construction industry.
- India: Though not a primary market, there have been instances where Indian companies have imported steel rebar from Iran, especially when local demand spikes.
3. Africa:
- West and North African Countries: Iran exports steel rebar to several African nations, particularly in regions where infrastructure development is a priority and where cost-effective construction materials are needed. Countries like Sudan and Egypt have been known to import from Iran.
- Kenya: As a part of the broader African market, Kenya has also imported steel rebar from Iran, driven by the demand for infrastructure development.
4. CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States):
- Azerbaijan: Due to its close proximity and shared borders, Azerbaijan is a notable importer of Iranian steel rebar. The country’s construction sector benefits from Iran’s competitive pricing.
- Turkmenistan: Another CIS country that imports steel rebar from Iran, supported by geographic proximity and trade ties.
5. Southeast Asia:
- Indonesia: Although not a primary destination, there have been instances where Indonesian companies have imported Iranian steel rebar, particularly when demand surges.
6. Other Markets:
- Turkey: Despite being a major steel producer itself, Turkey has imported steel rebar from Iran under certain trade conditions, particularly when prices are favorable.
- Qatar: Although Qatar has diversified its suppliers, Iranian steel rebar has been exported to Qatar, especially during periods of high demand in construction.
Iran’s steel rebar exports are influenced by factors like trade relations, restrictions, pricing, and logistical considerations. Despite facing challenges such as international restrictions, Iran continues to maintain and even expand its export markets for steel rebar.
8. What are the advantages of Iranian steel rebar compared to their competitors?
Iranian steel rebar has several advantages compared to its competitors, making it a preferred choice in many markets. These advantages include:
1. Competitive Pricing:
- Cost-Effectiveness: One of the primary advantages of Iranian steel rebar is its competitive pricing. Iran’s relatively low production costs, driven by cheaper labor, energy, and raw materials, allow it to offer rebar at lower prices compared to many competitors. This makes it particularly attractive in price-sensitive markets.
2. Proximity to Key Markets:
- Geographic Advantage: Iran’s location provides easy access to key markets in the Middle East, Asia, and parts of Africa. This geographic advantage reduces transportation costs and delivery times, making Iranian rebar more appealing to nearby countries like Iraq, Afghanistan, Oman, and others.
3. Adherence to International Standards:
- Quality Assurance: Iranian steel rebar is produced in compliance with various international standards, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), BS (British Standards), and DIN (German Institute for Standardization). This adherence ensures that the rebar meets the required quality specifications for different construction projects, making it competitive with products from other leading producers.
4. Consistent Supply:
- Stable Production: Despite international challenges, Iran has managed to maintain a consistent supply of steel rebar. The country’s strong domestic production capacity ensures a steady flow of exports, which is crucial for large construction projects that require reliable material supplies.
5. Customizable Grades and Specifications:
- Variety of Products: Iranian steel manufacturers offer a wide range of rebar grades and specifications, allowing customers to choose products that meet their specific needs. This flexibility makes Iranian rebar suitable for various applications, from residential construction to large-scale infrastructure projects.
6. Government Support:
- Export Incentives: The Iranian government supports the steel industry through various incentives, including subsidies and favorable export policies. This support helps keep production costs low and enhances the competitiveness of Iranian steel rebar on the global market.
7. Technological Advancements:
- Modern Production Techniques: Iranian steel producers have invested in modern production technologies, which improve the efficiency and quality of their products. These advancements help Iranian rebar compete with products from countries that have more established steel industries.
8. Adaptability to Market Demands:
- Responsive to Market Changes: Iranian producers are known for their ability to adapt quickly to changes in market demand and global economic conditions. This agility allows them to remain competitive even in volatile markets.
9. Environmental Considerations:
- Efforts to Reduce Environmental Impact: Although the Iranian steel industry faces environmental challenges, there are ongoing efforts to improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions. These initiatives can enhance the appeal of Iranian rebar in markets that prioritize sustainability.
In summary, Iranian steel rebar offers a combination of competitive pricing, high quality, reliable supply, and adaptability, making it a strong competitor in the global market. These advantages help Iran maintain and grow its market share despite the challenges posed by international competition.